Safe travels in Europe
The population of Europe in 2015 was about 742 million, approximately 11% of the entire world population. This makes it the fourth largest continent in terms of population. In terms of area, Europe is the second smallest continent (after Australia, or Oceania to be precise). It covers a total area of 10,400,000 km².
Climate
Europe has several types of climate. These are influenced by surrounding seas, the Apls and influences from the Arctic.
Western Europe
Western Europe has several types of climate: the south is subtropical and a small desert area. The south is usually warm and dry. Central Western Europe has a temperate climate, a sea climate. Northern Norway has an Arctic climate.
Northern Europe
The weather in Northern Europe can be influenced by arctic air or the supply of warm (summer) or cold (winter) air from the former Soviet Union. In Scandinavia, high-pressure areas can occur that hardly move.
Southern Europe
Southern Europe has, thanks to being close to the equator and influenced by the warm Mediterranean Sea, dry, warm summers and mild, wet winters. In some places, even in the coldest months, the weather can be like springtime for weeks.
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is the most erratic in terms of climate. The Balkan can be extremely cold in winter, very hot in summer and this region is often affected by flooding due to heavy rainfall, sometimes in combination with meltwater from the mountains.
Area: 10,400,000 km²
Population: 742 million
Climate: Varied
Tropical diseases in Europe
Dengue
No, dengue does not occur in Europe.
Yellow fever
No, yellow fever does not occur in Europe.
Malaria
No, malaria does not occur in Europe.
West Nile virus
Yes, West Nile virus occurs in Europe.
Zika
No, zika does not occur in Europe.
Dangerous animals in Europe
When you think of dangerous animals, you are probably thinking of predators in Africa, venomous snakes in the Middle East and deadly sea creatures in distant oceans. All these dangerous animals are far away, however, in Europe a few dangerous creatures can be found. The information below will help you with what to look out for and how to be prepared when travelling.
Ticks
Ticks live in forests, dunes, heathland, sheltered meadows, parks, and gardens. Particularly in tall grass and dead leaves. Ticks attach themselves to passing animals and humans. Ticks become active when the temperature rises above 7 degrees Celsius. People are bitten between March and October.
Ticks can transmit diseases, including Lyme disease. Prevent a bite with Anti-Insect and make sure to bring an (impregnated) travel mosquito net if you’re staying in a forested area. Insect repellent socks are also recommended when hiking; ticks come from below.
Have you been bitten? It is important to remove the tick as quickly as possible, within 8 hours, with a tick remover. Do not sedate the tick with alcohol, nor heat it with a cigarette. The tick will release its saliva in response and transmit bacteria that can cause diseases. You can disinfect the bite with alcohol. If you have removed the tick within 8 hours, the risk of infection will be minimal.
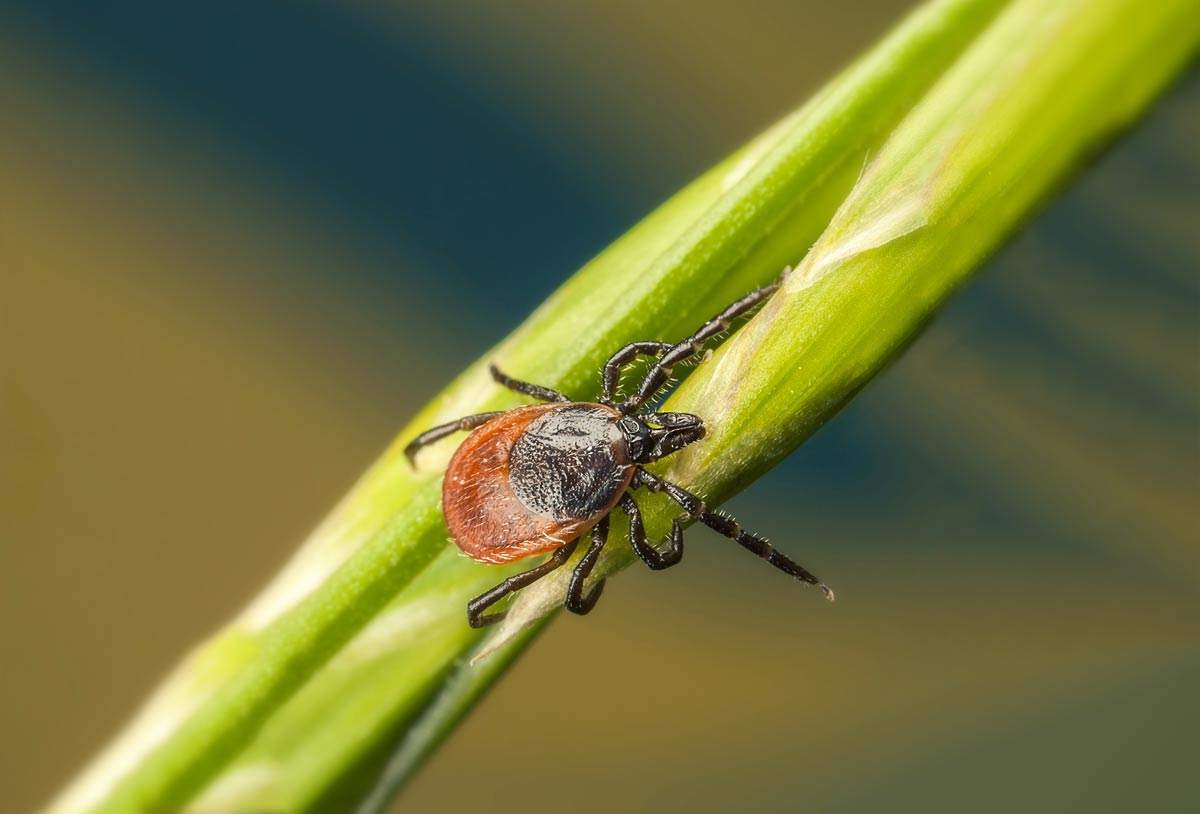

Sheep tick (Ixodes ricinus)
Spiders
The European black widow, the most venomous spider in Europe, fortunately, does not occur in the Netherlands, but mainly in Mediterranean countries. A small bite from the European black widow is enough to cause extreme pain and a chance of nausea, convulsions and arrhythmia. Watch out for this spider in areas around the Mediterranean Sea.
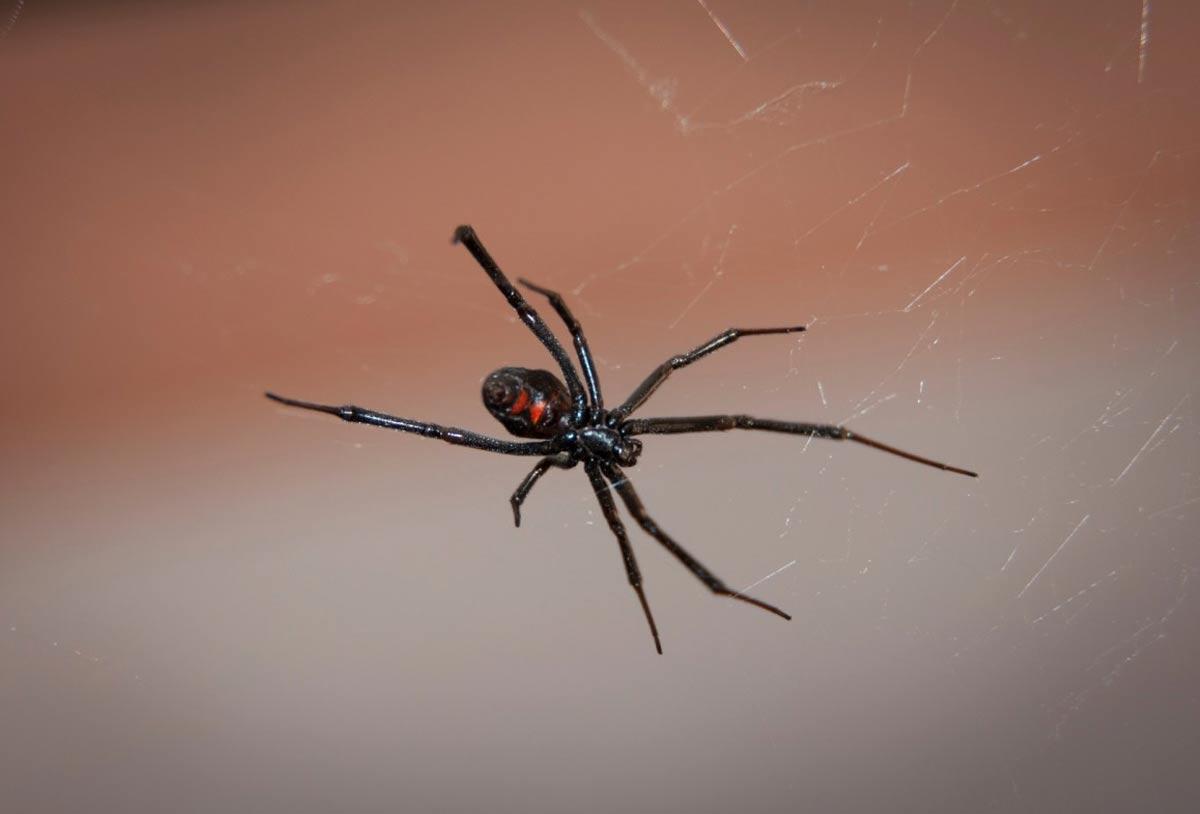

European black widow (Latrodectus tredecimguttatus)
Aspis viper
The most dangerous species of snake, the Aspis viper, lives mainly in southwestern Europe. Approximately 4% of the people who are bitten by them do not survive; many survivors get permanent damage to their eyes and liver from the poison of the Aspis viper.
This snake is found in France, Germany, Spain, Portugal, Italy and Switzerland. The habitat consists of steep ridges, humid mountain areas and forest edges with many open spaces. Preferably with fallen tree trunks or stones under which the snake can hide.
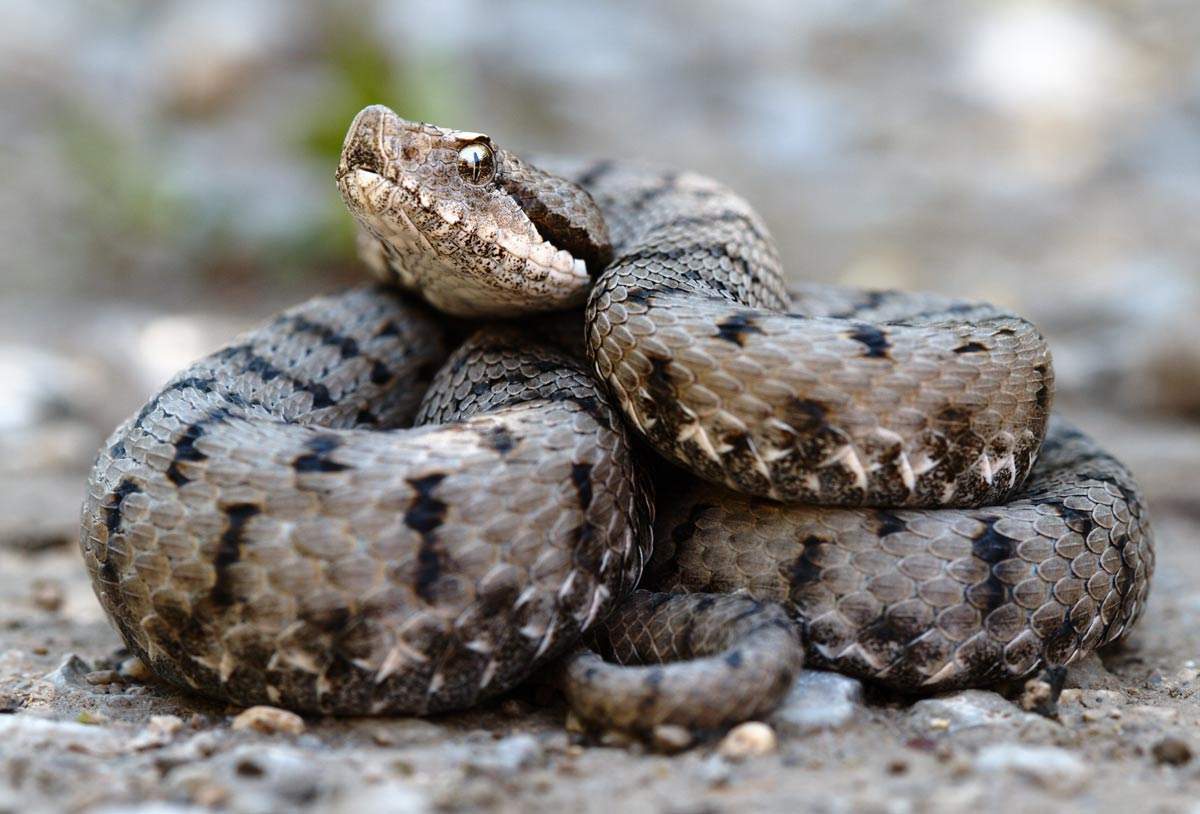

Aspis viper (Vipera aspis)
What to pack




Good to know
Vaccination
Most countries in Europe do not require vaccination, although for some countries it is recommended. Countries such as Malta, Belarus and Bosnia are a few examples.
Visa
You do not need a visa to travel to European countries.
Water
Tap water is safe to drink in European countries.
Language
Europe has 51 countries. The most commonly spoken language is German. German is spoken by 16% of the population. In second place are English and French combined, spoken by 13% of the population.